Key Community-Based Rehabilitation Programme
- Probation is a community-based sentencing rehabilitation option ordered by the Court when dealing with offenders who may otherwise be sent to penal or corrective institutions such as MSF Youth Homes, Reformative Training Centre, or the Prisons.
- Probationers can continue with most of their day-to-day activities such as school, work or National Service.
- Parental involvement and community support are key components in the probation process.
- The Probation Officer will regularly discuss the probationer's progress with the his/her parents, and school or employer and update the Court on the progress.
Probation Period
- Between 6 months to 3 years.
- Placed under the supervision of a Probation Officer or Volunteer Probation Officer.
Probation Conditions
The probationer is also expected to comply with conditions ordered by the Court, such as:
- Regular reporting to the Probation Officer
- Time restriction including a period of electronic monitoring, if necessary
- Community service
- Rehabilitation programmes tailored to probationer’s risks and needs.
Breach of Probation Conditions
- If the probationer does not follow the conditions of his Probation Order, he/she may be given warnings by the Probation Officer or taken to Court.
- The Court may warn the probationer, amend or revoke the Probation Order. If the Order is revoked, the Court can sentence the probationer for the offence for which he/she was placed on probation.
View annual reports of the Probation Service here
For More Info
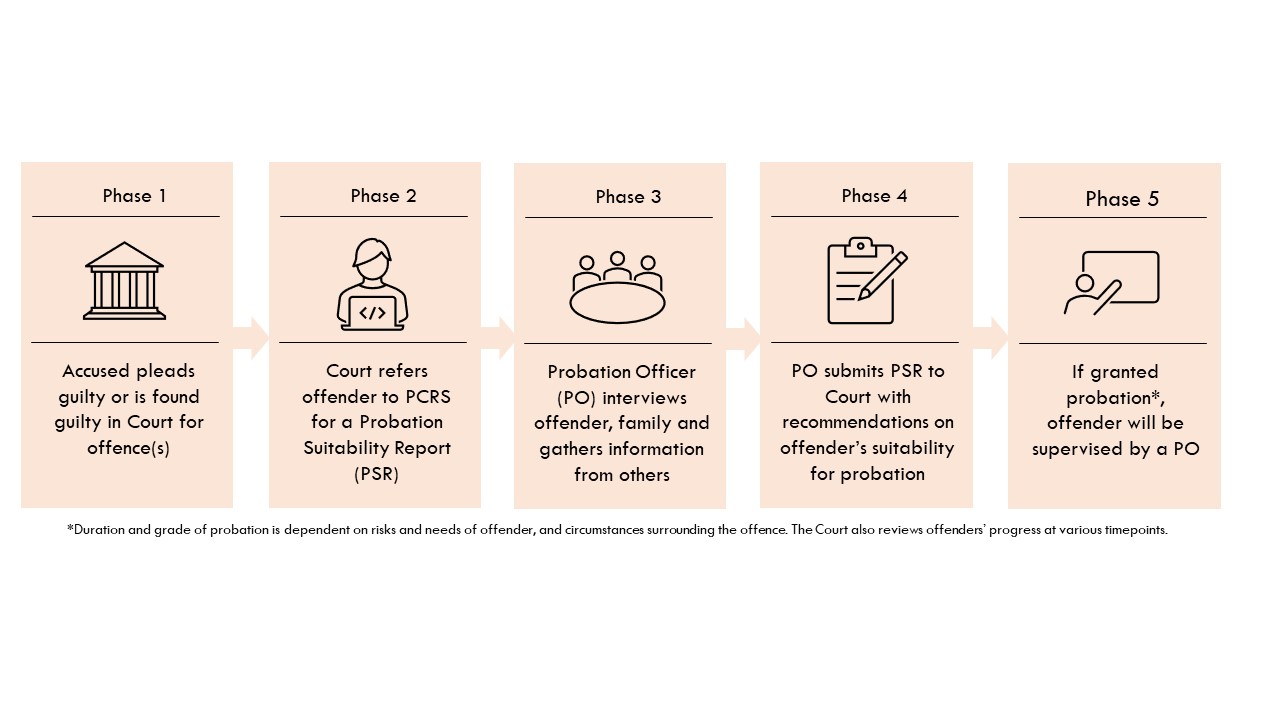
Flow chart showing the probation process. The probation period can last between six months to three years.
Victim Impact
To create awareness of the impact of crime on victims, encourage empathy including towards victims and thinking through consequences of their actions.
Law and Order
To educate probationers on common offences in Singapore and help them be cognisant of the need for law and order in society.
Life Skills
To impart necessary life skills such as emotional management, conflict resolution, problem solving, decision making and communication skills to enhance probationers' abilities to behave in a pro-social manner.
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
To equip probationers with skills to manage risky situations and avoid committing further offences.
Conflict Resolution
To help probationers understand how conflicts arise and introduce pro-social methods of resolving differences.
Parenting Programmes
To improve communication between parent and probationers for effective parenting and family support.
Probation Elective Programmes are considered essential or beneficial for certain probationers. Based on the nature of the offence, coping skills and needs, they will be selected to undergo the selected programme(s) at appropriate stages of their probation.
Offence-Specific Programmes
- Theft Intervention Programme (TIP): A comprehensive specialised group-based intervention for youths who have committed repeated theft offences. TIP focuses on helping youths develop skills to take responsibility for their offending behaviours, examine impact of their actions, identify personal offence cycles and craft a detailed self-management plan to stop their stealing behaviours.
- Violence Prevention Programme (VPP): VPP targets offenders assessed to be at risk of violent re-offending by challenging their cognitive distortions and equipping them with skills to manage their offending behaviours and to lead a positive lifestyle.
Family-Related Interventions
- Functional Family Therapy- Juvenile Justice (FFT-JJ): An evidence-based intervention programme designed to address complex family issues within the youth offender population. This strengths-based approach helps youth and their families reframe years of hurt and discord into their stories of hope and strength. The greater involvement of parents in the youth’s lives can then translate into more sustainable outcomes and prevent the youths from committing further offences.
- Mandatory Counselling: A mandated condition by the Youth Court requiring selected parents/probationers to undergo compulsory counselling sessions from agencies such as social service organisations. Parents are counselled on effective management of marital and parent-child relationship issues to provide an appropriate home environment for their child’s rehabilitation.
Other Programmes To Support Rehabilitation Of Offenders
- Prison Visit: An experiential programme that provides probationers a first-hand experience of prison life. It aims to help them cherish the opportunity for community-based rehabilitation and deter them from re-offending.
- Smoking Cessation Clinic: A programme held at schools or polyclinics to educate probationers who have committed smoking offences or with smoking habits on the dangers of smoking and strategies to quit smoking.
- Anti-Secret Society Talk: A seminar by conducted by the Singapore Police Force Secret Societies Branch for offenders with previous or current gang association. Parents are required to accompany the offenders. The objectives are to help offenders decline any gang involvement; and for parents to be vigilant to guide their child away from gang association.
- Anti-Drug Workshop: A workshop conducted by Central Narcotics Bureau for offenders with a history of experimentation with drugs. The workshop highlights the dangers of abusing drugs and shares ways for offenders to stay away from drugs.